Scenario:
Make: Cisco
Model: ASA 5506-X, ASA 5506 W-X, ASA 5508-X, 5500-X Series
Mode: GUI [ASDM]
Description: In this article, we will discuss the different types of logging and syslog configuration methods via ASDM on Cisco ASA. Refer to the article linked here if you are facing Cisco ASA Logging/Syslog Time Sync Issue.
Loggings
A method of collecting messages from devices to a server running a syslog daemon is called system logging. Logging to a central syslog server helps in aggregation of logs and alerts. Cisco devices can send their log messages to a UNIX-style syslog service. A syslog service accepts messages and stores them in files, or prints them according to a simple configuration file. This form of logging provides protected
long-term storage for logs. Logs are useful both in routine troubleshooting and in incident handling.
Syslog messages begin with a percent sign (%) and are structured as follows:
%ASA Level Message_number: Message_text
[ays_quiz id=’2′]
Syslog/Loggings Security Level
Syslog messages are divided into 8 categories and each category has a security level. We can assign custom colours to each of the severity levels to make it easier to distinguish them in the ASDM log viewers. The security level of Syslog messages is as below:
| Level Number | Severity Level | Description |
| 0 | emergencies | System is unusable |
| 1 | alert | Immediate action is needed |
| 2 | critical | Critical conditions |
| 3 | error | Error conditions |
| 4 | warning | Warning conditions |
| 5 | notification | Normal but significant conditions |
| 6 | informational | Informational messages only |
| 7 | debugging | Debugging messages only |
Note: The ASA and ASASM do not generate syslog messages with a severity level of zero (emergencies). This
level is provided in the logging command for compatibility with the UNIX syslog feature but is not used by
the ASA
Syslog Configuration on ASA via ASDM
Step1: Login
Login to the ASA using username and password.
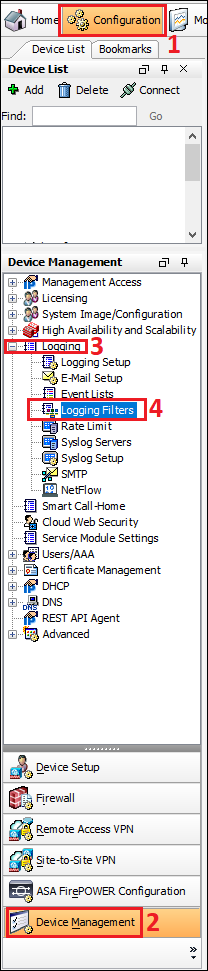
Step2: Logging Filters
Follow the steps shown below in the image to navigate to the Logging filters.
Step3: Logging Destination
Choose the name of the logging destination to which you want to apply a filter. Available logging destinations are as follows:
- Console port
- ASDM
- Internal buffer
- Telnet & SSH session
- SNMP server
- Syslog server
Configuring Logging Destination
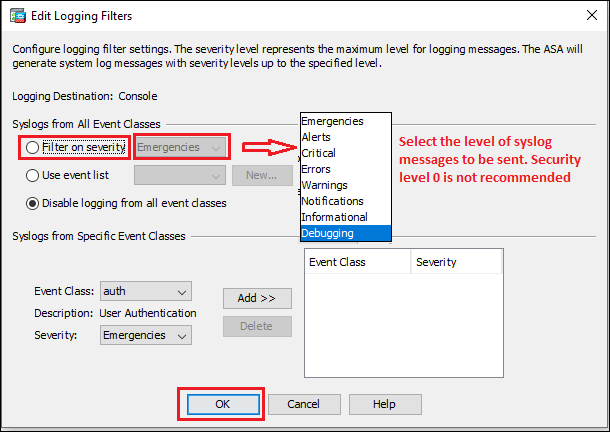
Step3a: Console Port
Syslog messages can be sent to the console port for monitoring. Follow the steps shown below in the image to configure syslog messages to be sent to the console port.
Step3b: E-mail
You could receive the Syslog messages by email as well. Configure the SMTP. Enter the destination e-mail address, and choose the Syslog severity level from the drop-down list.
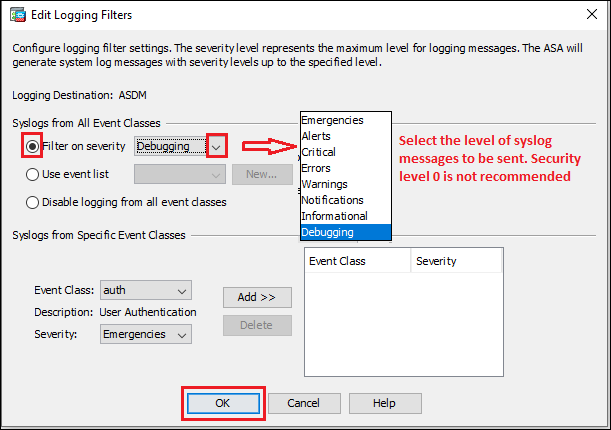
Step3c: ASDM
Syslog messages can be monitored on ASDM page. Follow the steps shown below in the image.
Step3d: Internal Buffer
Internal buffer servers as a temporary storage location that could be used to save Syslog messages. Define the internal buffer size and then follow the steps shown below in the image to configure syslog messages to be sent to internal buffer.
Step3e: Telnet & SSH Session
To send syslog messages to a Telnet or SSH session, follow the steps shown below. Make sure SSH or Telnet session is configured on ASA.
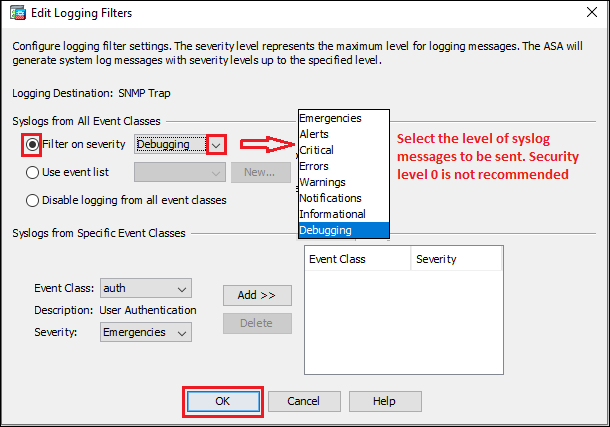
Step3f: SNMP Trap
Configure SNMP on the Cisco ASA and then follow the steps shown below in the image to configure syslog messages to be sent as SNMP Trap.
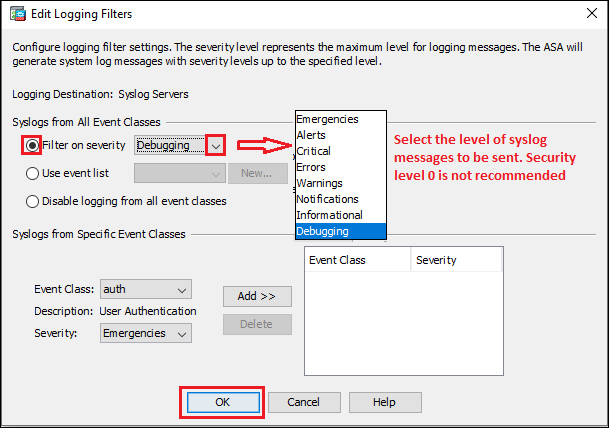
Step3g: Syslog Servers
Follow the steps shown below in the image to configure syslog messages to be sent to syslog servers.
You could configure ASA syslog or logging using the methods described above.
Other Topics on ASA
- Cisco ASA IOS Upgrade/Downgrade CLI
- Configure IP SLA on Cisco ASA Firewalls
- Configure Redundant or Backup ISP Link on Cisco ASA – CLI
- Add Static ARP or MAC Binding on Cisco ASA Firewall
- How to Configure VPN Between Microsoft Azure & Cisco ASA
Source: Knowledge Base, Internet, Cisco
EA00138